📚 Technology Stack
Python, BFS, DFS, Greedy, A*
📃 Details of the requirement
Given a maze map as shown in figure 1, where:
- The star symbol represents the starting position of the agent.
- The X symbol represents walls that the agent cannot move to.
- The + symbol represents reward points that the agent can collect by moving to these positions, which will reduce the cost of the path.
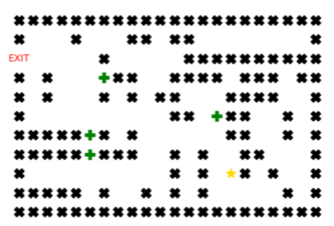
- The "exit" symbol represents the destination position that the agent needs to move to, which is the only position that the agent can escape from the maze.
The goal of the students is to implement algorithms to find the path from the starting position to the destination position (the position to escape the maze) for the agent. The agent can only move up, down, left, right with equal cost. You need to implement the following algorithms:
- Uninformed search algorithms:
- Depth First Search algorithm (DFS).
- Breadth First Search algorithm (BFS).
- Informed search algorithms:
- Greedy Best First Search algorithm (Greedy Best First Search).
- A* search algorithm.
For informed search algorithms, you need to define a suitable heuristic function for this problem. You can try different heuristic functions and report the results.
Regarding game maps, there will be two types: maps without rewards and maps with rewards. Your task is to implement search algorithms and design maps for both types.
- For the case of maps without rewards (80%), you will implement 4 algorithms to solve them. You will design and report about 5 typical maps (you should choose maps that the algorithms differ from each other) and compare the differences in pathfinding between these types of maps and each different strategy. Specifically, for a selected map to report, you will note:
- How the differences between search strategies for this map are shown? You need a map output with the path to illustrate and apply theory about the completeness and optimality of algorithms to explain.
- With search strategies that have information, you can choose different heuristic functions and report the differences between strategies for each heuristic function.
- For the case of maps with rewards (20%), you will think of ways to solve and propose strategies for the agent to move so that the cost of the path from the starting point to the exit point of the maze is as small as possible (note that the agent does not necessarily have to go through all reward points). You need to design a map with at least 3 cases: 2, 5, 10 reward points with different values on the map. If you cannot find the optimal solution (regardless of whether the number of reward points is many or few), propose a heuristic strategy to solve it, for example, greedily eating all reward points according to their values before finding a way out of the maze.
- The size of the selected maps for reporting must ensure that there is at least one large map (the length and width of the map must be at least 15 and at least 35, respectively).
- Minimum number of maps required for reporting and analysis: 5 maps for maps without rewards and 3 maps for maps with rewards.
Please refer to the map drawing function in the following notebook: link
Test scenario and map design
Each test scenario is designed as follows:
- The first line is the number of reward points n (n = 0 for maps without reward points).
- The next n lines will each include 3 integers x, y, z where x, y are the coordinates of the reward point in the matrix; z is the value of the reward point, which will be negative integers.
- The following lines describe the game map. Note that the end point of the journey will be the exit point from the maze (for example, in figure 2, the end point will be the point at row 2 and column 0); the starting point of the agent is marked with the character S; the characters x will be the walls; the characters + will be the reward points.
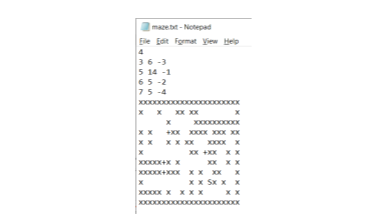
For example, with the file 'maze.txt' as follows: Note about maze exit point: Note that the maze map must be designed so that there is only one position on the edges of the map where the agent can exit. Output for each map: The result returned for each map will be a graphic representing the path and the cost of the path. An example of the resulting path drawing is shown in figure 3.